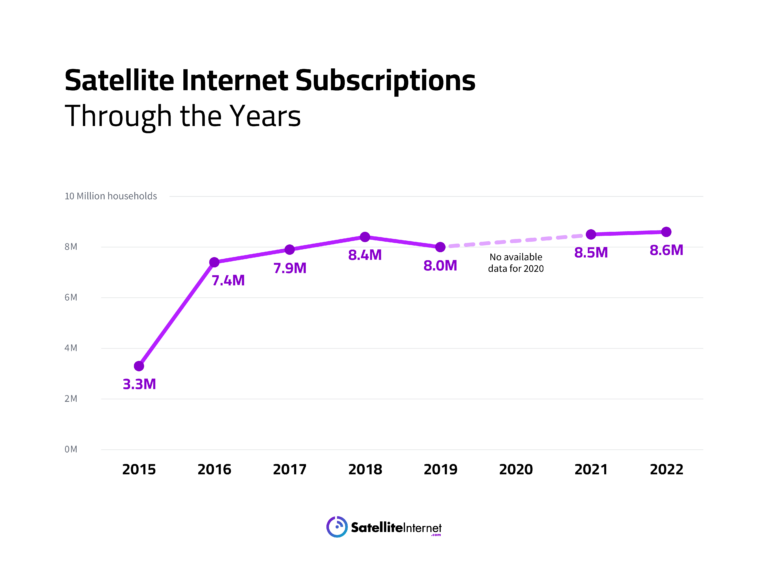
The number of people who have access to satellite internet has increased by 157% in the last seven years, according to U.S. census data.
The strong investment in and evolution of satellite technology in the past decade has made access to the internet a reality for practically everyone in the world.
To put these huge changes into perspective and explain why this is important, let’s consider the state of internet access in the United States right now.
- About 91.2% of people in the U.S. have access to the internet as of 2022, even though 95.7% of households have a computer.
- This leaves 8% of people without access to the internet.
- There has actually been a decrease in the number of households without internet by 57% since 2015, according to Pew Trusts research.
As you can see, while access to the internet has never been more widespread, there is still work to be done to ensure all Americans have the opportunity to access the web.
Many of the gaps in internet access occur in rural areas. One in four rural Americans still say that access to broadband internet is a problem in their community. As of 2022, about 13.8% (46,108,315) of Americans live in rural areas, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
As of early 2024, the Federal Communications Commission defines broadband internet as a connection that provides bandwidth of at least 100Mbps download speed and 20Mbps upload speed. All three major satellite providers offer plans that meet that definition.
The Federal Communications Commission tracks data on internet availability across the country with its broadband map. Here’s the breakdown.
0.1% of people use dial-up
Good, old-fashioned dial-up internet was the first type of internet connection offered to most American consumers. As you can see, it’s nearly extinct, with most providers having upgraded their infrastructures with better, faster technology. It’s also not fast enough to be considered broadband.
6.7% of people use satellite internet
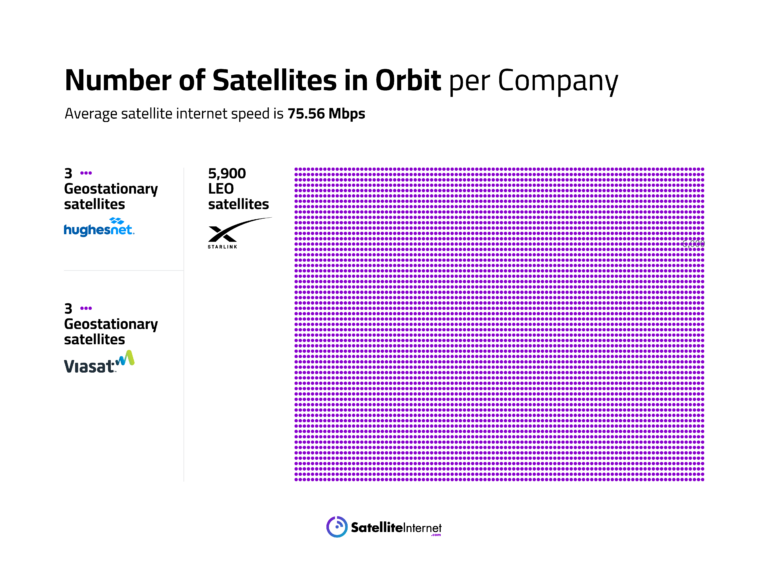
It’s by far the most accessible type of provider. Thanks to both geostationary orbit and low-Earth orbit satellites, satellite internet is available almost anywhere in the U.S. However, it does have several things working against it.
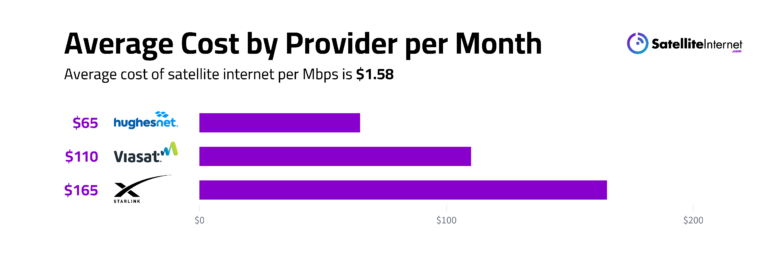
While satellite is widely available, it’s also one of the most expensive options for internet access. This is due to the high costs of launching satellites and the limited number of companies providing internet access to consumers. Also, it’s among the slowest, due to the high latency involved in satellite internet.
11.2% of people use 5G or fixed wireless internet
This is wireless internet provided mostly by cellular companies. Besides satellite, it is the best option for people in rural areas. Using signals delivered to a home receiver from a cellular tower, some providers require specialized equipment to capture a signal. Most receivers require a clear line of sight to a tower for adequate signal, so it’s not widely available in especially rural areas with no towers, or mountainous and forested areas.
75.9% of people use wired internet (cable, fiber, or DSL)
Wired internet types are currently the most common and fastest available internet. Delivered via a wired connection through phone line, coaxial, or fiber wiring, these internet types require specially built infrastructure. Rural communities are less likely to have these infrastructures built, and it takes a lot of investment—from the providers themselves or from public sources—to build them. That’s why satellite is usually the only option for rural households.